
Knee replacement surgery can give you new life and the freedom to be as mobile as you once were. But the invasive procedure has risks that include infection and knee replacement failure. If you still have mild to moderate knee pain, call a vascular specialist in Brooklyn NY instead. Dr. George Bolotin at the Astra Vein & Fibroid Treatment Center is an experienced interventional radiologist who performs a remarkable new treatment called knee embolization. It’s minimally invasive and has been proving to be successful when performed by an expert. Don’t wait until your knee pain is excruciating. You may even be able to avoid surgery altogether by calling a prestigious vein clinic in Brooklyn.
When your knee joint becomes severely damaged from arthritis or injury, it causes intense pain and a reduced ability to walk, climb stairs or participate in ordinary daily activities. Knee replacement is a surgical procedure in which damaged cartilage and bone are replaced with metal and plastic implants to restore knee function and alignment.
Knee replacement is usually only recommended after other forms of treatment fail to provide pain relief. An effective alternative is knee embolization, a minimally invasive procedure that blocks blood supply to the lining of the knee, potentially delaying or eliminating the need for knee replacement. If you need a knowledgeable and experienced interventional radiologist and vein doctor in Brooklyn for knee embolization or other vein treatments, the best option is the vein center in Brooklyn at Astra Vein & Fibroid Treatment Center.
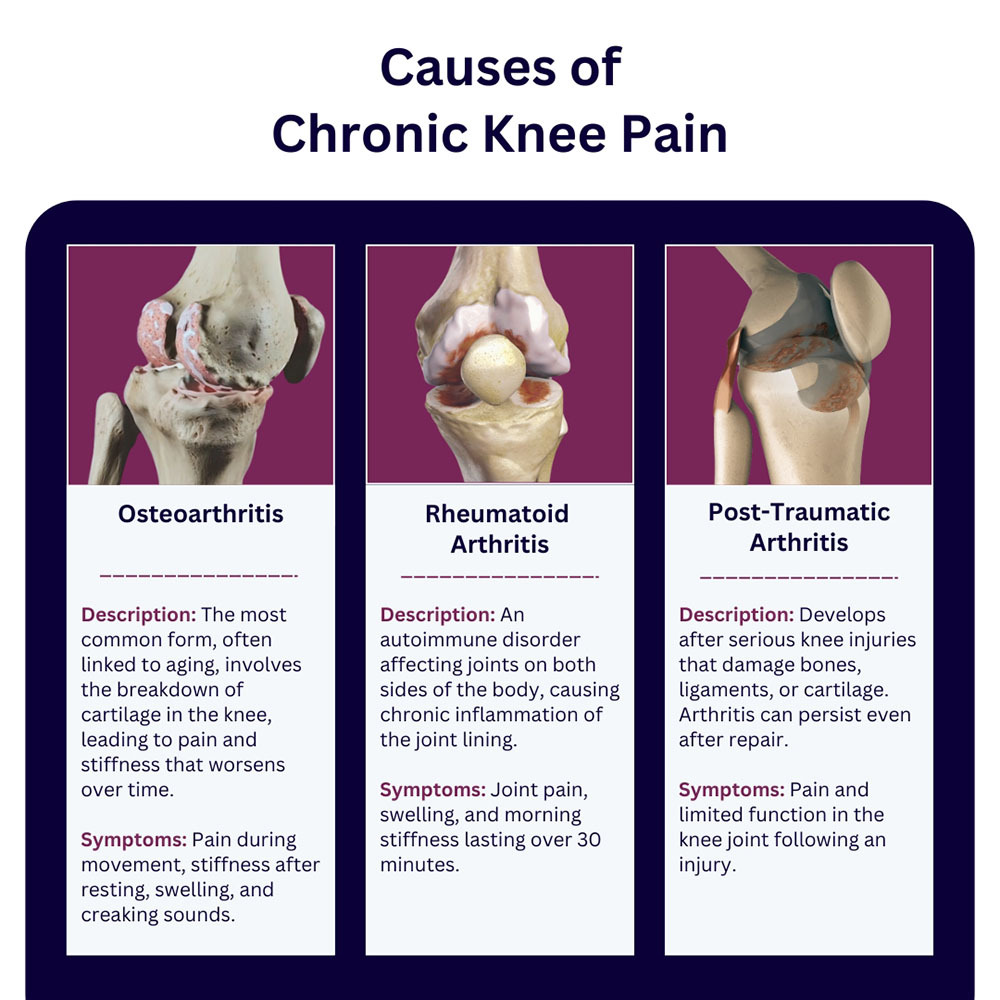
One of the most common causes of knee pain is arthritis, a term used to describe conditions characterized by joint inflammation that’s persistent and chronic. A variety of forms of arthritis can lead to chronic knee pain and stiffness, including:
When one or both knee joints are affected by arthritis, pain usually develops gradually and intensifies as time passes.
Other symptoms you may experience include:
Knee pain from arthritis may come and go. As the condition progresses, pain becomes more constant. Your risk of developing arthritis increases if you’re obese, there’s a family history of arthritis or there’s repetitive stress or injury to your knee, such as from running or working in a demanding job that keeps you on your feet all day.
More conservative forms of treatment are usually tried before your vascular specialist in Brooklyn recommends knee replacement.
Factors that indicate you may need a knee replacement include:
To determine whether a knee replacement is right for you, your NYC doctor checks the range of motion, strength and stability of the knee joint. X-rays and other imaging tests help your doctor view the extent of your knee joint damage.
If a knee replacement is the best option for you, your surgeon tells you how long before surgery you should stop eating and drinking.
Steps of a knee replacement include:
The procedure usually takes one to two hours, and you may have to stay in the hospital for a day or two. Knee replacements can be partial or total. In a partial knee replacement, only the damaged part of the knee is replaced. It may be two or three months before you can resume normal activities and up to a year before you fully recover. Factors affecting the length of your recovery include your age, your overall physical condition and how well you follow the instructions of your doctor and physical therapist.
Knee replacement is an invasive procedure with long recovery times and several potential complications such as infections, blood clots and reduced range of motion. If your pain isn’t severe, there are several other things to try before going forward with major surgery.
These include:
When none of these options relieve your knee pain, talk to a vascular specialist in Brooklyn to find out if knee embolization is a good option for you. Knee embolization may be able to provide pain relief and improved knee function without the need for traditional surgery at this time, especially if your pain is still at a low or moderate level.
For more information on knee embolization or varicose vein treatment in Brooklyn, contact Astra Vein & Fibroid Treatment Center. When you visit this vein clinic in Brooklyn, you can count on quality care, personalized attention and the most up-to-date treatment options.
Vein & Vascular Medical Care
4209 Ave U, Suite A.
Brooklyn, NY 11234
(347) 934-9068
Vein & Vascular Medical Care
869 E Tremont Ave
Bronx, NY 10460
(929) 447-4563